
Data Communication Networks
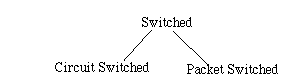
Packet switched nets are store and forward nets.
ckt switched nets have dedicated communication paths (i.e. telephone)
For example:
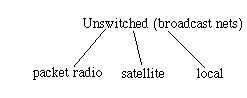
A Broadcast Comm. Net can be WAN, the media is unshared:
LAN Examples:
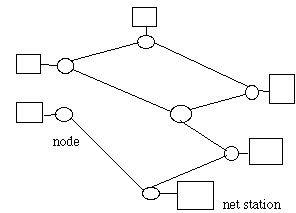
Ethernet with a bus topology:
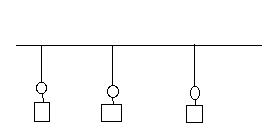
Ring topology net:
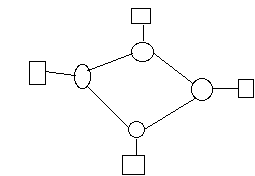
Note: no switching nodes, media is shared in LAN
For packet radio, every station can hear every other, the media is shared so this is a LAN technology.
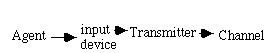
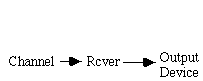
This course addresses the communication systems parts between the input and output devices.
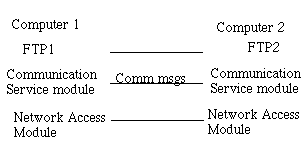
Computer Communications Architecture
The Three Layer Model
Application run on computer which use networks
network layer - xchange of data between computer and network
transport layer - error detection and correction
application layer - file xfer etc.
File xfer modules
xmits passwords
file commands
file records
communications service module
error correction
encryption
keeps track of data to ensure delivery
Network Access Module
net specific stuff

(SAP) service access points 1 2 and 3 are used to uniquely identify the application communicating
Network access layer is told which computer but not which SAP
The transport layer will break data into chunks adds control information and this is called a PDU or protocol data unit
Protocol Data Units
TPDU1 = transport protocol data unit :=
transport hdr, chunk1
TPDU2 = transport hdr, chunk2
NPDU = network protocol data unit = network hdr, TPDU
Application data = chunk1 + chunk2 + ...
Destination SAP (service access points)
TPDU has destination SAP so that appropriate application obtains data
Sequence # TPDU's may be sent in any order, and by different routes and may arrive at different times.
TPDU may have error detection or correction codes built-in
NPDU
destination address (i.e. IP address)
facilities requires (i.e. priority)
Transmission Terminology
point-to-point :- guided transmission is unshared
I.e. O(N**2) connectivity (completely connected)
![]() = number of
links
= number of
links
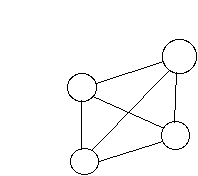
Multipoint guided transmission allows shared medium
ANSI Defs:
simplex - one direction only
half-duplex - two-way but not at the same time.
full-duplex - simultaneous two way transmission
CCITT
CCITT vs ANSI
simplex = half-duplex
duplex = full-duplex
CCITT = international telegraph and telephone consultive committee
Analog and Digital Data Transmission
data - entities which convey meaning
signals - encoding of data
signaling - act of sending a signal
transmission - communication of data by propagation and processing of signals
digital data - takes on discrete values, i.e. text integers.
analog data - takes on continuously varying patterns of intensity, i.e.. sound
But what is digital? What is Analog? How do we defines these things?
s(t) is continuous (i.e. analog) iff
![]()
for all a
A signal, s(t) is discrete iff
![]()
for some a
For example, the function s(t) has multiple values or does not exist and there fore the limit does not exist.
Let the function f be defined on the set S. f is continuous at a point P0 of S iff
![]()
whenever ![]() .
.
If f is defined on an interval [a, b] and is continuous at ![]() then given an
then given an
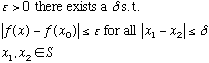
Data and Signals
Modem (modulator/demodulator)
modulation involves two waveforms: The modulating signal (the message) and the carrier wave which is altered by the modulating signal
The complementary process is called demodulation
Bits <-> modem <-> analog signal <-> modem <-> bits
Codec := coder-decoder
analog <-> codec <-> bits
In General a digital waveform has infinite bandwidth.
Band limited channels low-pass filter square waves, this rounds their corners.
Rule of thumb: if a signal is W bps, you may need 2W Hz bandwidth.
Sigal Strength
attenuation := a loss of signal strength
signal strength falls off logarithmically so the decibel is used to measure the loss
Decibel gains and losses are computed via simple addition and subtraction.
Let ![]() number of
decibels
number of
decibels
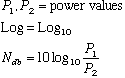
Example:
![]()
loss=10log(5/10)=-3 dB

![]()
dBw=decibel watt
![]()
![]()
![]()
About Those Exponents...
The Laws of Exponents give us the laws of logarithms
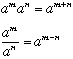
![]()