3.3 Analog Data, Digital Signals
A/D conversion-digitization
After the signal is digitized you can do:
1. Xmit via NRZ-L (Nonreturn-to-Zero-Level)
2. encode via another method, then xmit
3. modulation of the data via a codec (coder-decoder)
PCM
Nyquist rate = 2 the highest significant signal frequency
The Nyquist rate results from the sampling theorem (see appendix 3A)
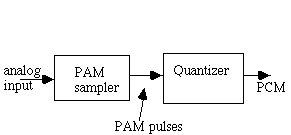
<Figure 3.11>
Pulse amplitude modulation (PAM) samples a wave form at regular intervals and creates an amplitude whose value is equal to the input signals amplitude at the instant of the sample.
PCM is obtained via quantization of PAM into one of a fixed number of levels.

The encoder which PCM may feed will take advantage of a priori knowledge of the channel, i.e. Sony F1.
The quantizer introduces quantization noise. It has about 6 dB per bit of S/N. For example, a 16 CD player has about 6*16=96 dB of S/N.
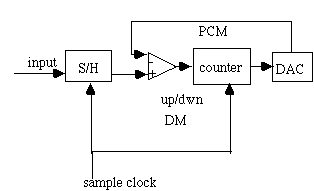
Delta Modulation (DM)
motivation :- improve PCM performance.
PCM encodes the value of each sample, DM only encodes the sign of the difference between the analog input and the reconstructed wave form after a sampling interval.
DM output may be used as the input to an up-down counter whose clock frequency equals that of the sample clocks.
DM may be obtained using the comparator output of a successive
approximation A/D converter.
round-off = quantization -> quantizing error
quantizing error = difference between the input voltage and the quantized voltage. For an n-bit ADC [Carlson 81]
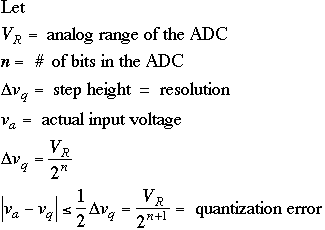
For DM, quantization error = quantizing noise for a slowly varying waveform.
Slope-overload error results in DM when the input signal slope is greater than the resolution times the sample frequency:
![]()
To compensate you could increase ![]() but then you increase the
quantization error.
but then you increase the
quantization error.
You could try to increase the sample rate, but then the bandwidth requirement increases. For this reason Adaptive DM may be used.
ADM step size is a function of the waveform history. For a given bit rate, ADM S/N is often higher than PCM for voice (bursty data).
ADM may increase slope as a linear function of time, but when the input signal slope changes suddenly, overshoot results and several sample clock periods are needed for large slopes to decay. This introduces spurious high-frequency components which may be removed via low-pass filtering.
" DM demodulation is simpler than PCM demod.
3.4 Analog Data, Analog Signals
The AM Equation:

suppose the input signal is a cosine wave:
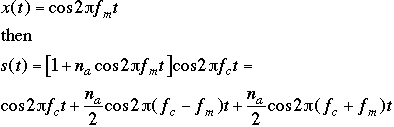
Proof: DSBTC (double sideband transmitted carrier)
![]()
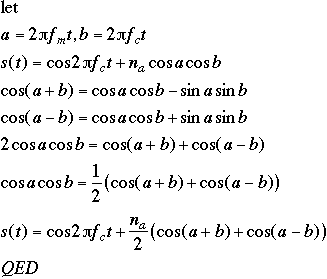
As the modulation index varies from 0 to 1 the depth of modulation varies from 0 to 100%. 100% modulation is the max permissible by the FCC. For more than 100% modulation the AM envelope dips below zero and distortion results (an envelope detector cannot recover the phase reversal information). Worse yet, the additional sideband amplitude can cause co-channel interference.
SSB removes the carrier and a sideband. This narrows the transmission bandwidth and power required to broadcast. W/O carrier and a sideband, phase information and synchronization is lost.
VSB introduces a reduced power carrier and a bandlimited upper sideband to allow phase reconstruction (synchronization). Since 50% of the DSB transmission power is in the carrier:
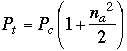
DSBSC double-sideband suppressed-carrier modulation is used.
Angle Modulation
PM and FM are AKO Angle Modulation (AKA exponential modulation). The angle modulation equation is:
![]()
for PM

for FM
![]()
![]()
![]() Hz
Hz
![]()
![]() which is m(t) invariant
which is m(t) invariant
Example
let ![]() be the phase-modulating signal, find s(t)
be the phase-modulating signal, find s(t)
![]()
by subst.,
![]()
note that the peak phase deviation is ![]()
let ![]() and we get:
and we get:
![]()
