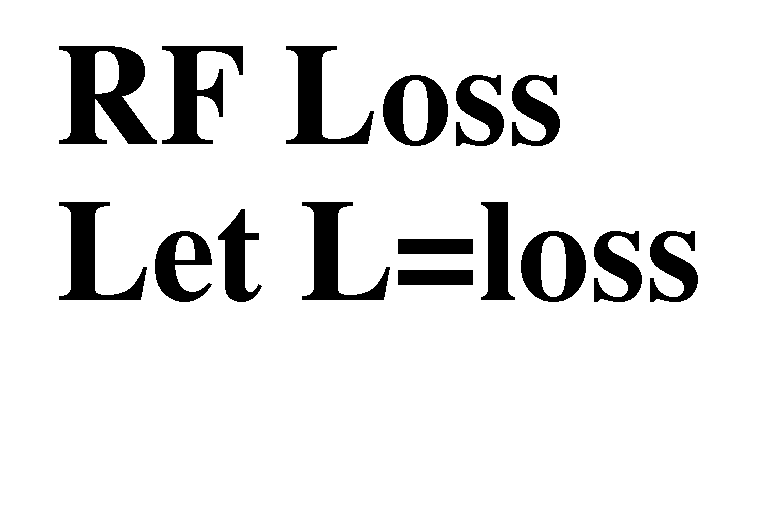
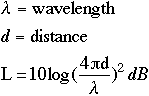
ISO-OSI Model
ISO= International Standards Organization
OSI = Open Systems Interconnection
OSI Model = a 7 layer model used to describe most networks today [1]
" 1. Physical Layer
This is a physical connection between machines. Electrical functional and mechanical specs are given here.
2. Data Link Layer
Provides reliable xfer of information across the physical links. Synchronization of frames, error control and flow control
3. Network Layer
isolates upper layers from net-specific item like establishing, maintaining and terminating connections in a switching network.
4. Transport Layer
error recovery and flow control
5. Session Layer
Control for communication, close and open connections
6. Presentation Layer
Data representation consistency; EBDIC -> ASCII, little endian to big endian
7. Application Layer
User Interface; i.e. kermit, ftp, appleshare file server, telnet, NFS mounts etc.
Transmission
Analog transmission -: a means of transmitting analog signals without regard to their content; e.g., binary data that passes through a modem
Digital transmission, a system which is concerned with the content; e.g. patterns of one's and zero's are recovered before retransmission.
noise is not cumulative in a digital transmission.
Digital transmission is the current trend, for voice and video.
Advantages are in digital technology, data integrity, security, capacity utilization and integration.
Transmission Impairments
* Attenuation and attenuation distortion
* delay distortion
* noise
Attenuation
For guided transmission Signal strength falls of logarithmically as a function of distance
Attenuation is an increasing function of frequency
Signal to noise ratio must be great enough
delay distortion :- velocity of a signal, in a guided media, is a function of its frequency. This causes intersymbol interference in digital transmissions and limits the maximum bit rate.
Noise
noise -: Undesired signals. Human interference (other communication systesm, ignition and commutator sparking, 60 cycle hum..) Natual noise-producin phenomena (atmospheric disturbances, extraterrestrial radiation and circuit noise..)
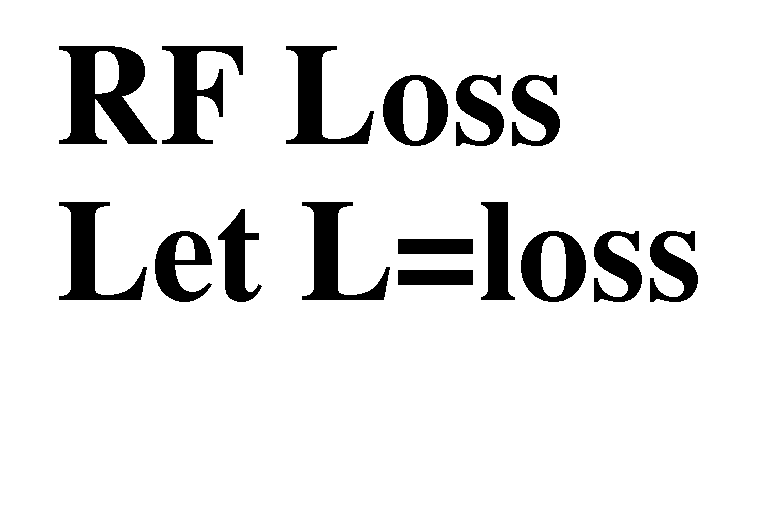
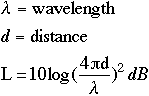
![]()

Mathematics of the fourier series
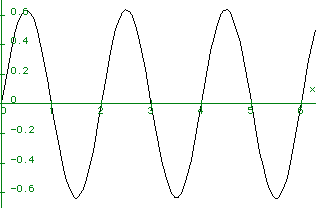
plot(f,x=0..2*Pi);
A sine wave:
sin(Pi x)
f := 2 ---------
Pi
the five term sawtooth wave:
f := 2 (sin(Pi x) - 1/2 sin(2 Pi x) + 1/3 sin(3 Pi x) - 1/4 sin(4 Pi x)
+ 1/5 sin(5 Pi x))/Pi
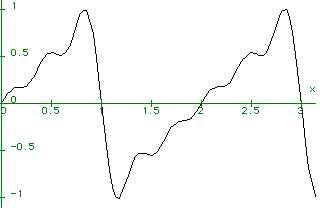
The ten term sawtooth wave:
f := 2 (sin(Pi x) - 1/2 sin(2 Pi x) + 1/3 sin(3 Pi x) - 1/4 sin(4 Pi x)
+ 1/5 sin(5 Pi x) - 1/6 sin(6 Pi x) + 1/7 sin(7 Pi x) - 1/8 sin(8 Pi x)
+ 1/9 sin(9 Pi x) - 1/10 sin(10 Pi x))/Pi
and
For the 100 term sawtooth wave:
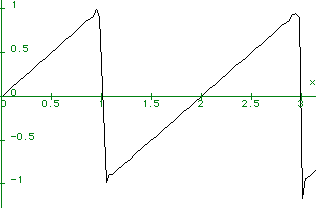
For K terms in the sawtooth wave:
K
----- (n - 1)
(-1) sin(n Pi x)
) -----------------------
/ n
-----
n = 1
f := 2 -----------------------------
Pi
Fourier series
:= an expansion of a periodic function as a series of trigonometric functions. Thus,
f(x) = a0 + (a1 cosx + b1 sinx) + (a2 cos 2x + b2 sin2x) + ...
where a0, a1, b1, b2 etc are constants called Fourier coefficients.
The series was first formulated by Jean Baptist Joseph de Fourier (1768-1830) and is used in harmonic analysis (fourier analysis) to determine the harmonic components of a complex wave.
Sine-Cosine Representation
![]()
![]()
![]()
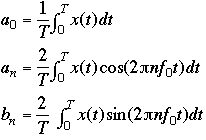
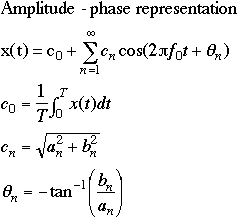

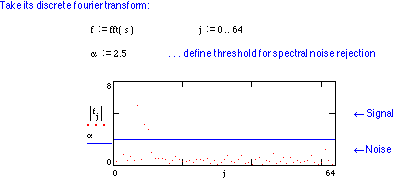
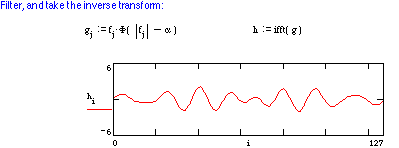
Power Spectral Density and Bandwidth
Time-limited signals have infinite bandwidth.
Effective bandwidth := the width of the spectra which contains the most power.
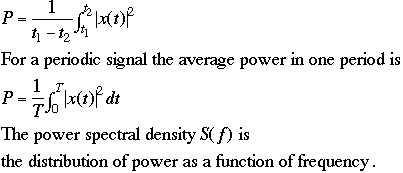
You will not be asked to compute PSD.